Drugs are essential for modern medicine therapeutics. However, despite their undoubted benefits, they may be responsible for many allergic reactions. The drug allergy is related to the awareness of the body either directly by the drug itself is most often by metabolites derived from this drug. It is seen in 10% of drug taken.
Allergic reactions are modulated by many factors :
The chemical structure of the drug
The way of introduction
Dose
Intermittent or continuous nature of the administration
Intercurrent pathology
And genetic factors
The clinical manifestations
Manifestations may occur during the first few hours the first day or the first weeks of treatment and may also occur after several previous treatments without allergic reactions. Several events may be suggestive:
Allergic reactions to anaphylactic shock type that can be fatal
Urticaria and facial edema
Digestive symptoms (nausea, abdominal cramps, vomiting, diarrhea)
Respiratory (cough, difficulty breathing, sneezing, runny nose)
Itchy eyes with redness
Eczema more or less extended in extreme cases can evoke a broad and deep burn.
The most involved drugs are penicillin, aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. But any drug may be responsible.
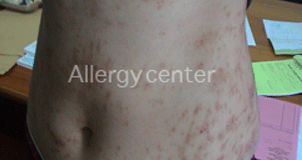
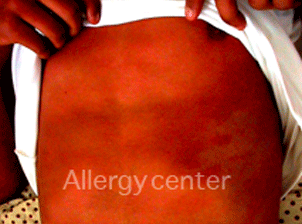
Delayed allergy to augmentin.
Diffuse skin lesions spared the face.
Persistence of pigmented lesions after taking several months.
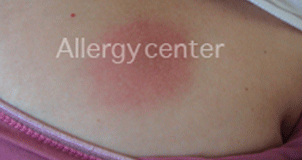
Fixed pigmented erythema after taking antibiotics (Clamoxyl).
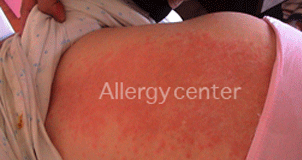
Allergic reaction to the application of an antiseptic chlorhexidine-based.
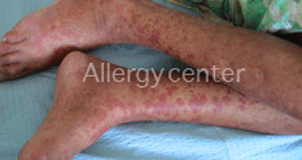
Immuno-allergic purpura after taking sulfonamides.

Urticaria induiced by paracetamol
CENTRE TUNISIEN D'EXPLORATION DES MALADIES ALLERGIQUES
Means of exploration
The allergy exploration based on four elements:
1. The evaluation of the degree
of accountability of the drug in the occurrence of adverse effects:
The liability of a drug may be suspected by the nature of the clinical manifestations and the chronology of events (time after the start of treatment, or compared to the last shot, as well as the notion of a possible increase in symptoms during another outlet.
2. Skin tests:
It is mostly intradermal reactions that help the positive diagnosis. They will be made four to six weeks after the allergic reaction and specialized environment because alone they can induce severe anaphylaxis.
The predictive value of tests varies from medications.
Test patches can also be made at delayed reactions.
3. Laboratory tests:
The tests are few and generally not validated except IgE to certain drugs like penicillin, insulin and curare.
4. Tests reintroduction in specialized areas:
Any reintroduction can only be done by a specialized environment and when skin tests are negative in patients with clinical responses in a questionable allergy context.
The protocol is variable depending on the drug involved (there is a different protocol for each drug).
This test called the oral challenge is done under medical supervision.
Test positive to 100 mg of aspirin provocation in a patient who experienced a coma after taking several drugs at once.
ALLERGY TO ANAESTHETICS
A. THE LOCAL ANAESTHETICS
Local anesthetics may cause allergic-type events after local injection (pruritus, urticaria, malaise). A possible vagal shock or hyperventilation syndrome occurring after the local anesthetic decision should not be confused with an immediate allergic reaction.
Intradermal tests with immediate reading (lidocaine 1%) are useful, but they must be at a concentration of 1/1000 to 1/10000 times. It is also important to go test all other local anesthetics looking for a cross-allergy.
B. THE GENERAL ANESTHESIA
Despite the progress in clinical and biological fields, it is difficult to prevent and even predict allergic accidents general anesthetics. The so-called “at risk” population remains unclear and very broad. Product managers are numerous, but the means of action for the time being limited.
a-Risk factors:
1.The sex: allergy to anesthetic affects more females and mainly concerns: the muscle relaxants (sex ratio 4/1 at 8/1).
2.Age: The risk is generally higher in the second, third and fourth decades. But anaphylactic shock can be observed at all ages.
3.Atopy: this risk factor remains to this day widely discussed and controversial. Atopy is considered by some authors as a risk factor for allergic intraoperative indisputable while others say the opposite.
4.The drug allergy drug allergy mediated by IgE and authentically demonstrated seems to be a possible risk factor
5.Asthma: It is recognized that non-stabilized asthmatic subject is a patient at risk of intraoperative bronchospasm
6.The number of previous general anesthesia well tolerated and previous exposure to anesthetics: the number of previous general anesthesia well tolerated does not seem to be a risk factor for promoting a reaction to relaxants muscle.
7.Abnormal ability to histamine release, anxiety, stress, hyperventilation: these factors are responsible for an increase in non-specific histamine release with clinical consequences.
b-aggravating factors:
1.Treatment with beta-blockers: taking beta-blockers is an aggravating factor of all anaphylaxis including anaphylactic shock anesthetics. Indeed, they are characterized by severe hypotension and bradycardia with a relative resistance to adrenaline.
2.Valvular heart disease: Can be responsible for various arrhythmias from worsening the clinical picture.
3.Pregnancy: it would complicate shocks due to dextrans
c-The clinical manifestations caused by an allergy to anesthetics are variable, ranging from simple redness to shock with cardiac arrest
d-Responsible officers:
All products used at the waning of anesthesia may be responsible: relaxants muscle, hypnotics, morphine, antibiotics, latex …
Shock following spinal anesthesia.
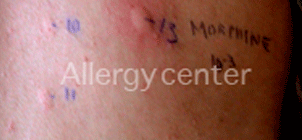
Positive to morphine diluted 1/1000 IDR.
Cefaloject allergy and muscle relaxants.
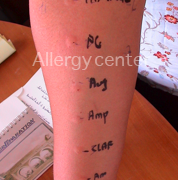
ALLERGY TO ANTIBIOTICS
Allergy to antibiotic is relatively common and asthma is not more exposed than others.
The intradermal reactions have sufficient reliability for a certain type of antibiotics and this as well as immediate reading delayed. Elsewhere patch tests and provocation tests may be tempted in a specialized environment.
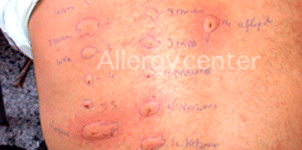
Reaction after taking penicillin.
Positive to all B lactams.
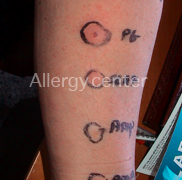
Reaction after taking penicillin.
Positive to intradermal reaction o all B lactams.
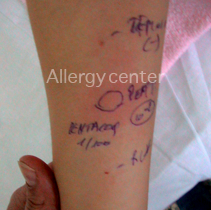
Pentacoq positive test in a patient who had a vaccine reaction at the age of 3 months.
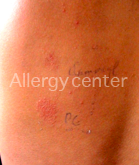
Positive patch tests to penicillin G.
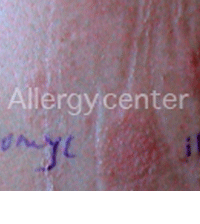
Positive patch tests to neomycin.
Patch testing positive to clamoxyl and negative to claforan.
Clamoxyl delayed skin reaction.
ALLERGY TO INSULIN
The allergy to insulin is rare. It is a real problem for the diabetic subject. It is most often immediate local reactions may sometimes generalize and give systemic reactions. They are the result of the production of IgE anti-insulin. Delayed reactions may also occur and are usually associated with contaminants. The intradermal reactions can confirm the diagnosis and to guide the prescription of insulin other classes. Furthermore desensitization specialized environment can be attempted.
ALLERGY TO ASPIRIN AND ANTI-INFLAMMATORY STEROID
Allergy to aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is a fairly common condition.
There are:
A combining form-nasal polyposis and asthma, aspirin intolerance called: Fernand Widal disease. In this case the use of aspirin is associated with a very severe asthma attack often. It is estimated that 10% of asthmatics suffer from this disease.A form which is manifested by the appearance of hives and swelling mainly of the face and eyes after taking aspirin or any nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
The diagnosis is based on the practice of a challenge test with aspirin in this specialized environment and under strict medical supervision.
The treatment is based on preventive and inflammatory nonsteroidal strict and definitive rejection of any aspirin or anti inflammatory drug.
Swelling of the face and lips after taking aspirin.

Allergic reaction after taking aspirin.

MANAGEMENT OF ALLERGY DRUG
First, it involves the processing of the current episode. Then after confirmation of the diagnosis
Systematic reporting in pharmacovigilance center.
Wearing a card allergic.
Delivery to the patient medication lists to exclude and possible alternatives.
Finally the possibility of induction of desensitization exist for drugs where no alternative is satisfactory.